Adenoid vs. Tonsil Problems: How to Tell the Difference
Introduction
If you often deal with sore throats, blocked noses, snoring, or frequent infections, you may have heard the terms adenoids and tonsils. Since they are often discussed together, it can be confusing.
Are they the same? Do they cause similar problems? And how do you know which one is responsible for the symptoms?
In this blog, we break it down simply so you can understand the difference between adenoid and tonsil problems, what signs to watch for, and when it may be time to seek medical advice.
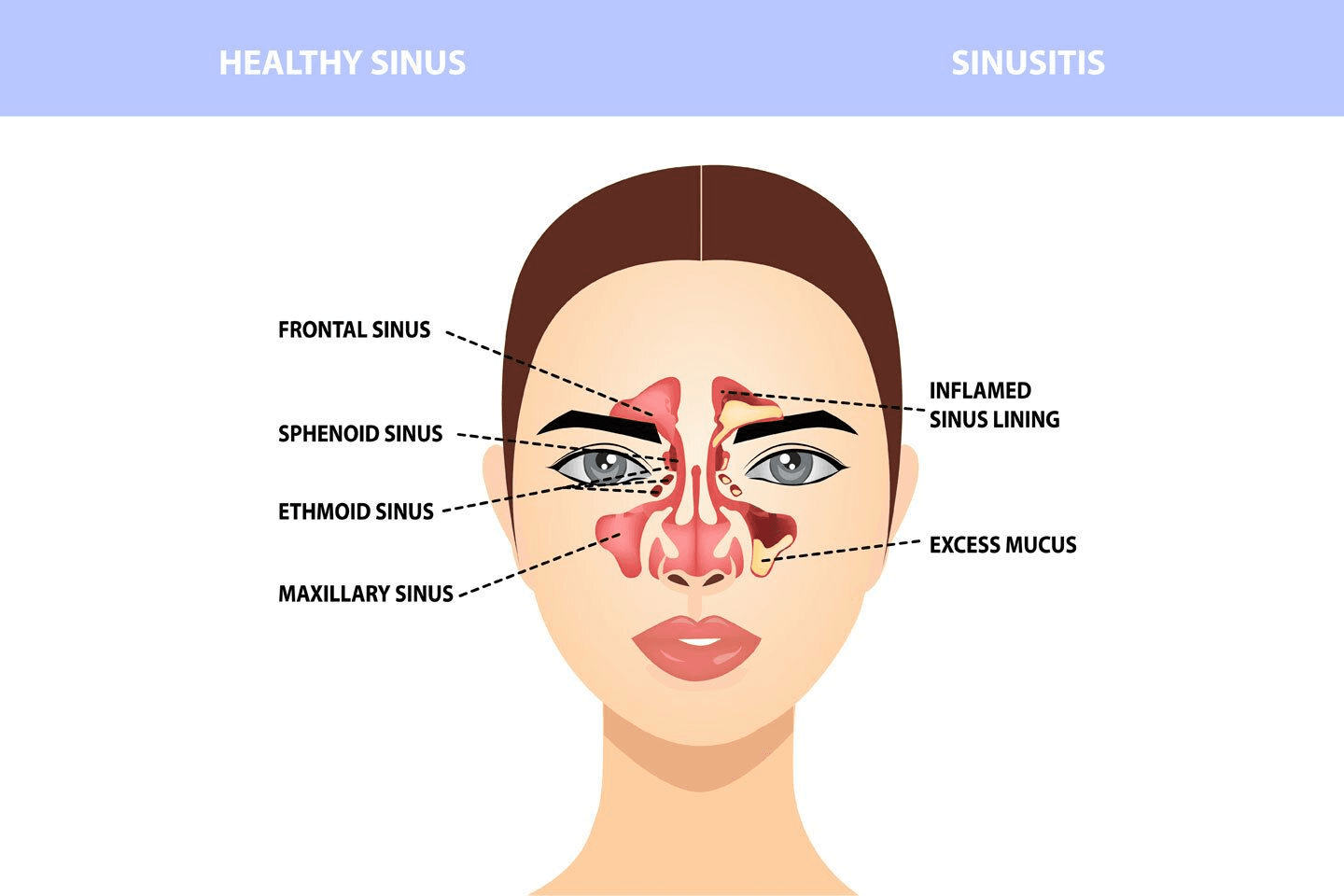
Where Are the Adenoids and Tonsils Located?
Adenoids and tonsils are part of your immune system, but they sit in different places.
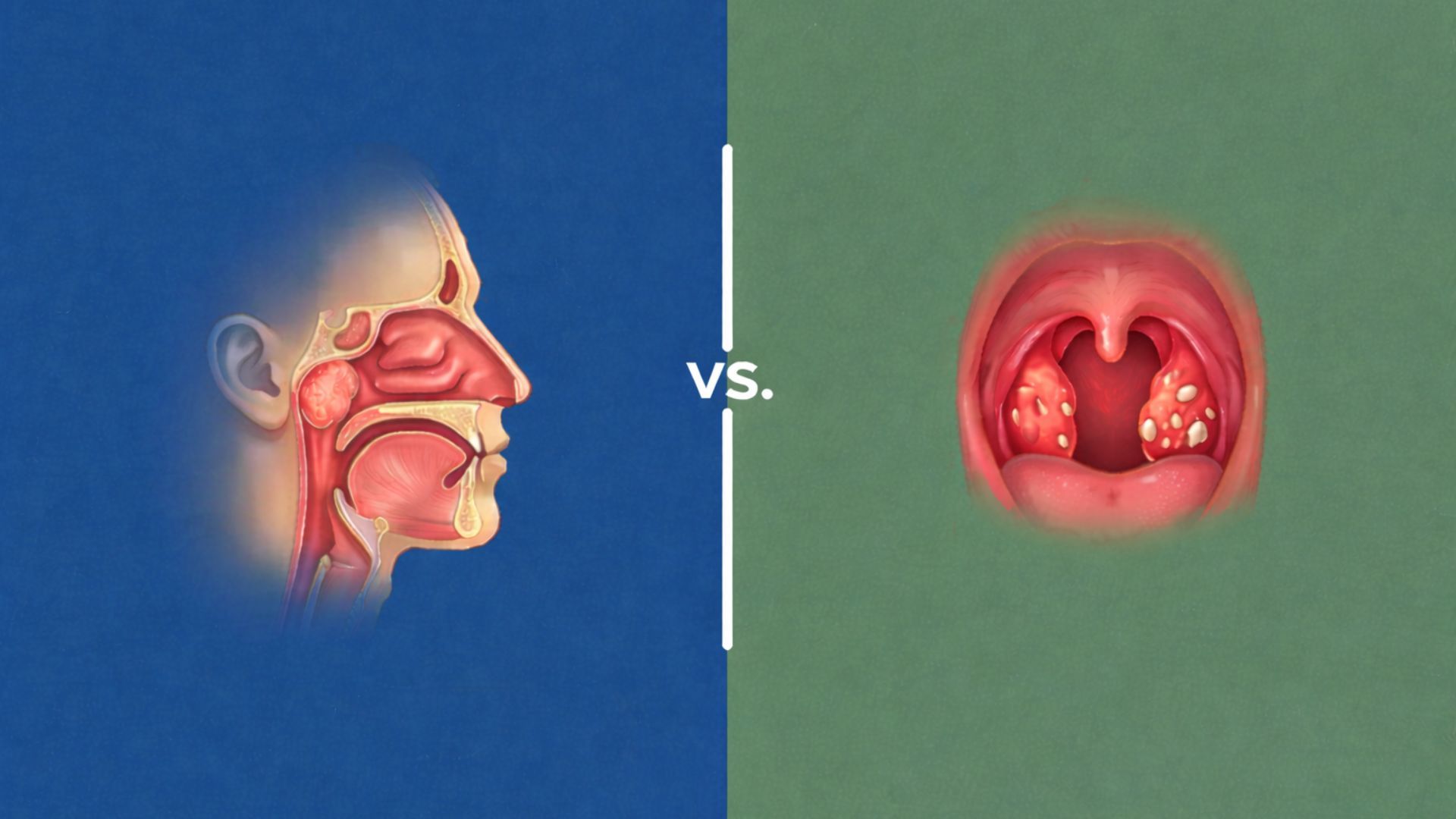
- Tonsils: two oval-shaped lumps visible at the back of the throat (one on each side). [1]
- Adenoids: located higher behind the nose and above the roof of the mouth, so you cannot see them just by opening your mouth.[2]
What Is Their Function?
Adenoids and tonsils act as part of the body’s first line of defence, especially in childhood. They help trap germs like bacteria and viruses that enter through the mouth or nose.
In young children, these tissues are more active as the immune system develops. As children grow older, adenoids and tonsils usually shrink and become less significant.
Tonsil Problems
Tonsil problems are common, especially in school-aged children and teenagers, but adults can also be affected.
Tonsillitis (inflamed tonsils)
Tonsillitis is often caused by a viral or bacterial infection.
Common signs of tonsil problems include:
- sore throat that worsens when swallowing
- red, swollen tonsils
- white or yellow patches on the tonsils
- fever and fatigue
- bad breath
- ear pain (referred pain from the throat)[2]
✅ If there is throat pain, fever and difficulty swallowing, tonsils are often involved. Consulting a doctor can help confirm the cause and guide treatment.
Adenoid Problems
Adenoid issues are more common in children, especially those below seven years old. Since adenoids sit behind the nose, their symptoms often affect breathing and nasal health.
Enlarged or infected adenoids can block airflow, leading to mouth breathing, especially during sleep.
Common signs of adenoid problems include:
- frequent nasal blockage
- mouth breathing during the day and night
- snoring or noisy sleep
- nasal-sounding speech
- recurrent ear infections
- disturbed sleep or restlessness[2]
✅ If a child snores loudly every night and breathes mostly through the mouth, enlarged adenoids may be involved.
How to Tell the Difference
A simple way to understand the difference is to look at where symptoms are strongest:
- Throat-related symptoms (pain, difficulty swallowing, visible swelling) → usually point to tonsils
- Nose/breathing symptoms (blocked nose, snoring, mouth breathing, ear issues) → often point to adenoids
However, sometimes both tissues may be involved.
When Both May Be Involved
In some cases, adenoids and tonsils enlarge together. This condition is called adenotonsillar hypertrophy.
A child may have:
- snoring and mouth breathing
- frequent sore throats
- sleep problems or pauses in breathing
- repeated infections
This may affect sleep quality, behaviour, focus, and learning if left unaddressed.
When to Seek Evaluation
Occasional infections are normal . But a medical evaluation may be needed if:
- Symptoms return frequently
- Breathing is affected regularly during sleep
- Snoring is loud and persistent
- Repeated ear infections or hearing issues occur
- Sleep is poor, and daytime tiredness develops
Early assessment may prevent complications and improve comfort and quality of life.
How These Issues Are Assessed
Doctors use:
- medical history review
- physical examination
- imaging (in selected cases)
Tonsils can usually be examined during a throat check. Adenoids may require specialised tools, such as a small nasal camera or imaging, because they are not directly visible.
Conclusion
Adenoid and tonsil problems can feel similar at first, but they usually affect different areas:
- Tonsil problems mainly cause throat pain and swallowing discomfort
- Adenoid problems mainly affect breathing, sleep and nasal health
If symptoms persist or interfere with daily life, professional evaluation is always recommended. Early understanding and timely care can make a meaningful difference.