Coronary Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Introduction
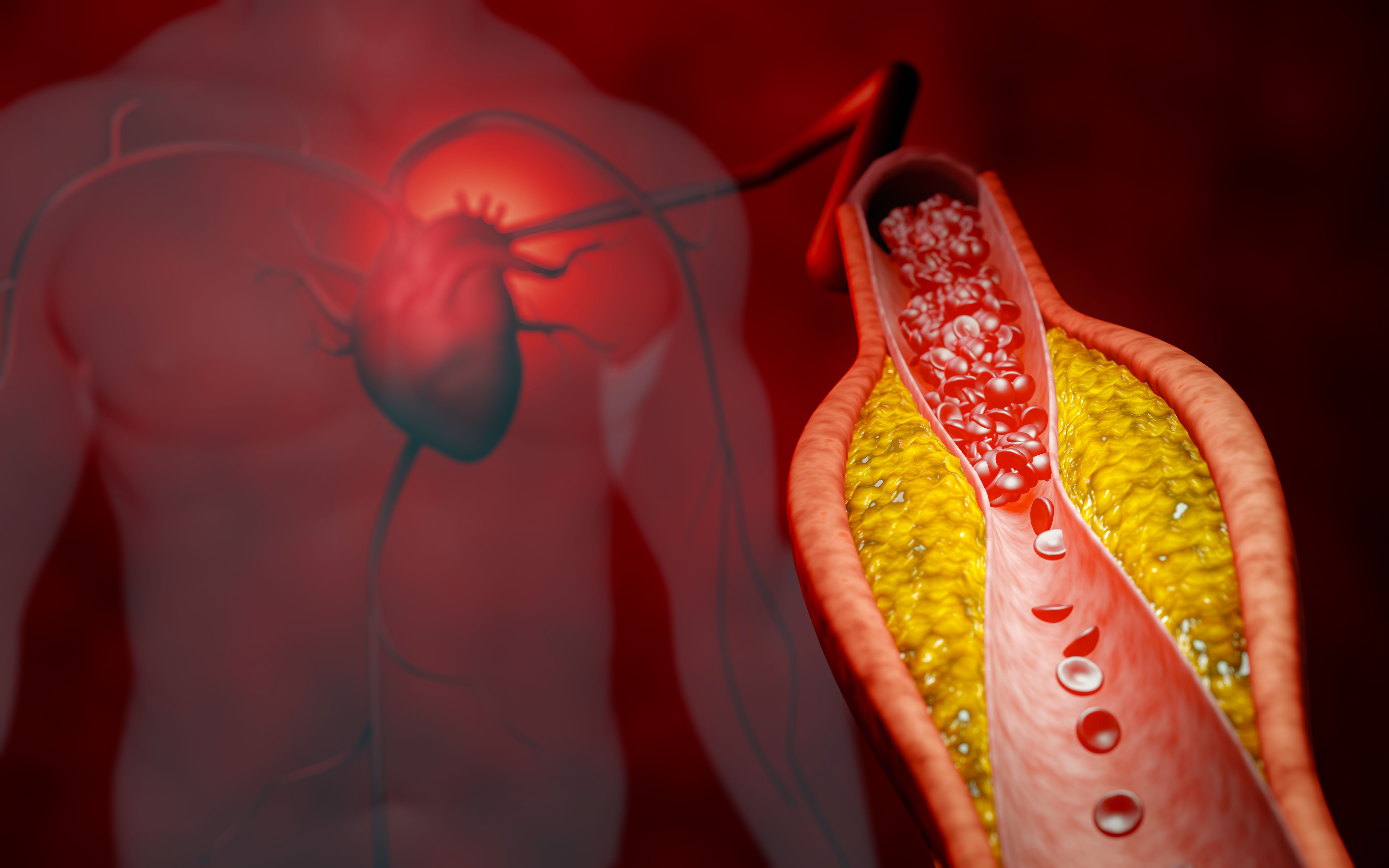
Narrowing or blockage of the heart’s arteries due to plaque causes Coronary Artery Disease (CAD). Coronary arteries deliver blood and nutrients to your heart, making it possible to work at its best1. If these arteries are damaged or blocked, the cells of the heart lack enough oxygen or nutrients to carry out basic biological processes, leading to cardiac muscle damage. CAD begins through a process called atherosclerosis, and this causes your coronary artery walls to become slowly inflamed and damaged. As time goes on, these damaged spots collect fatty deposits, cholesterol and other materials, creating plaque that makes arteries narrower and sends less blood to the heart2. If not treated in time and diagnosed correctly, CAD can lead to several potentially fatal cardiovascular problems, such as myocardial infarction (or heart attack). Coronary artery disease often progresses over a number of years, so one might not notice an issue until he/she have a significant blockage or a cardiac arrest. However, one can adopt several methods to prevent or reduce the risk of coronary artery disease. Switching to a healthy lifestyle could make a major impact.
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease
Modifiable Risk Factors
These can be managed through lifestyle and medical care:
- High blood pressure: Causes the arteries to work much harder.
- If there are high levels of cholesterol, it encourages plaque buildup.
- Using tobacco and smoking injures the artery walls and means there is less oxygen reaching your blood.
- High blood sugar due to diabetes eventually damages blood vessels.
- Heart strain occurs with obesity and it is common for it to appear together with other risk factors.
- Lack of exercise weakens the heart and increases other conditions that lead to CHD.
- Unhealthy food choices often contain lots of saturated fats, trans fats and sodium.
- Long-term stress: Can cause blood pressure to go up as well as increase other risk factors
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
These cannot be changed, but knowing them helps you stay vigilant:
- Risk of stroke goes up with a person’s age (men at 45 and women at 55 or older)
- Men frequently develop coronary artery disease before women do.
- Genes passed through the family are a possible risk for heart disease.
- People from particular racial/ethnic backgrounds have a higher risk.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
The most common signs of CAD include:
Chest pain (Angina) – It is the most common sign of CAD. It could be felt as a pressure, tightness or discomfort in the chest area. Angina is usually triggered by strenuous physical activity or emotional stress. In some cases, the pain may be short or sharp and felt in the neck, arm or back region.
Shortness of breath - When the heart is unable to pump enough oxygen carrying blood to meet the body's requirements, the person is likely to experience shortness of breath or severe fatigue.
Other Signs: Weakness, nausea, light-headedness and cold sweat.
For a detailed breakdown of the 3 major symptoms of CAD, read our blog: 3 Major Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
How CAD is Diagnosed
Non-Invasive Tests
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG):
- What it is responsible for: Recognition of the electrical pulses in your heart
- Expect to have electrodes put on chest, arms and legs without pain or discomfort.
- Duration: 5-10 mins
- It displays the rhythm, rate and any previous episodes of heart attack.
Echocardiogram:
- How it does it: Uses sound waves to make movies of your heart’s movement
- Stringy gel gets spread on your chest and the transducer passes back and forth over the area.
- The session usually runs for 30-60 minutes.
- The images display how the heart is structured, works and routes blood through it
Performing a Stress Test:
- How it works: Checks the heart as it is working during physical activity
- Expect to walk on the treadmill while an ECG monitor is taking your readings.
- Time: 15-30 minutes.
- Indicates: How effectively your heart adjusts to being asked to work harder
Advanced Imaging:
- This study is a cardiac CT scan.
- Calcium buildup and plaques formed in coronary blood vessels
- May involve injecting patients with contrast dyes.
Invasive Procedures
Coronary Angiogram:
- What it helps with: Produces detailed pictures of the coronary arteries
- A doctor inserts a slim tube (catheter) into an artery in your wrist or groin.
- What blockages: It clearly indicates the spot and degree of the obstruction
Treatment Options for CAD
Lifestyle Changes
Heart-Healthy Diet:
- Choose to eat lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean protein.
- Avoid eating a lot of foods with saturated fats, trans fats, sodium and added sugars.
- Following the Mediterranean or DASH diet could be helpful.
Regular Body Movement:
- Exercise moderately at least 150 minutes each week.
- Integrate sessions that are both aerobic and strengthening
- Begin with something easy and then make your workouts harder.
Smoking Cessation:
- It is consistently the most significant step for smokers.
- Speak to someone trained in mental health if necessary.
- Quitting brings advantages within 24 hours.
Stress Management:
- Do relaxation activities (meditate, practice deep breathing)
- Try to join therapy or stress management courses.
- Try to keep a good balance between your job and personal life.
Medications
Drugs that may be used are:
- Antiplatelet medications (such as aspirin) are given to stop blood clots.
- Using statins helps reduce cholesterol.
- ACE inhibitors used to lower blood pressure
- Medicines called beta-blockers help relax the heart and lower its strain.
- Using nitrates can ease chest pain.
Procedures and Surgery
When lifestyle changes and medications aren't enough:
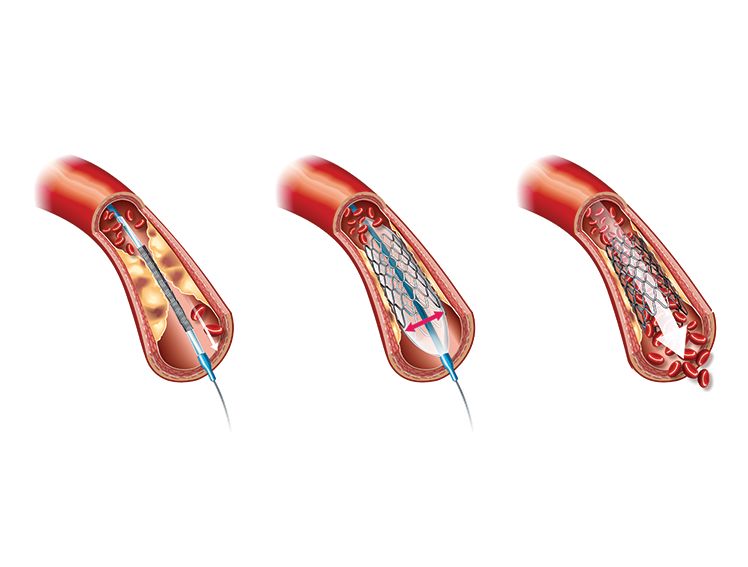
Angioplasty: A unique inflatable balloon is mounted on a catheter, which is inserted into the blood vessel with the blockage. When the catheter reaches the blockage or plaque build-up, it inflates the balloon to push the blockage radially outwards, clearing the blood vessel passage to secure proper blood flow. This is called balloon angioplasty. Angioplasty is a procedure to widen the coronary arteries and restore the blood flow.
Meril’s Evermine50 is a stent used in angioplasty and has the following features:
- Ultra-low strut thickness of 50μm for promoting early vascular healing
- Variable strut width and variable crown design to ensure adequate radial strength of 1.1bar*
- Hybrid cell stent design: Open cells in the middle of the stent for side-branch access and closed cell design on ends for optimal scaffolding and conformability
- Clinically established drug everolimus with biodegradable polymer for proven clinical safety & long-term efficacy
Our specialized Bioresorbable Scaffold – MeRes100 is classified under Sirolimus Eluting BioResorbable Vascular Scaffold System. It has the following features: -
- Next Generation BioResorbable Scaffold: World's first 100µm BVS
- Ideal strut thickness to minimize vascular injury & ensure early endothelialization
- Virtual Tubing: Couplets of tri-axial RO markers at either end of the scaffold
- Hybrid Stent Design: Strut width variability allows for adequate radial strength
- Future treatment possibilities: Restore the artery to its natural state after resorption
Coronary artery bypass surgery: A graft is created to bypass the blocked coronary artery, using a blood vessel from another part of the body. It restores blood flow to the heart by diverting the flow of blood around a section of a blocked artery in the heart. Since this requires an open-heart surgery, it is most often reserved for cases where there are no other less invasive methods clinically advisable.
Conclusion
The risk of a cardio vascular disease is different for different people. The symptoms are easily mistaken for just fatigue. Do not ignore the warning signs. Get it diagnosed and be ahead to enjoy every moment of your life and add more to life. It is never too late to adopt a healthier lifestyle.