Soft Tissue Injuries: Find the Types & Treatment Online
What are soft tissue injuries?
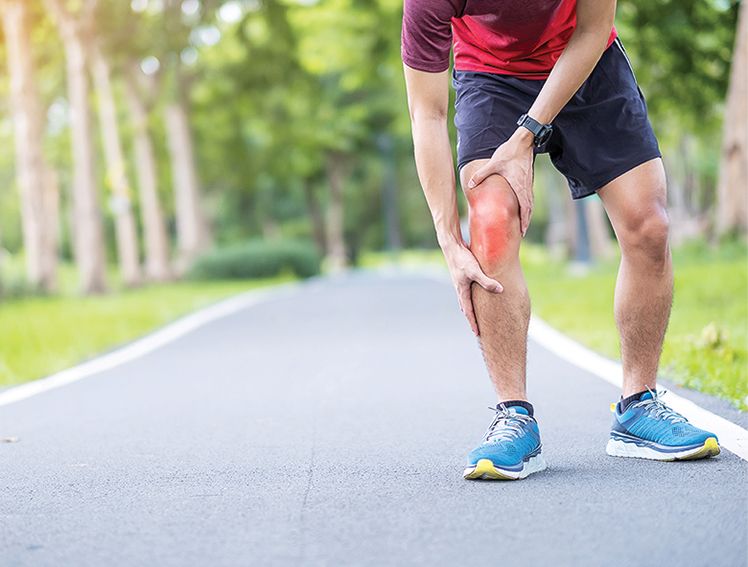
The body's soft tissues include the muscles that enable movement, the ligaments that connect bones, and the tendons that attach muscles to bones. When these tissues get stretched, torn, or damaged from sudden movements, overuse, or direct impact, this is called a soft tissue injury.[1] Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected area normally. Such injuries are very common and can happen during daily activities, sports, or work.[2]
Today, we will look at some common soft tissue injuries and explore available treatment options.
Sprains
A sprain is a tear in your ligament due to a sudden movement that causes the area to twist. The treatment for a sprain depends on the severity of the injury. A mild sprain can be treated through the RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) techniques. A severe sprain usually needs surgery. Patients might have to go through physical therapy as well.
Bursitis
Your body has tiny, fluid-filled sacs known as bursae. The bursae help in minimising friction during movement. Bursitis is a condition in which the bursae get inflamed. Bursitis generally occurs in the elbow, knee, foot, and hip. The RICE technique helps in treating bursitis, though some patients may also need anti-inflammatory medicines and physical therapy. In more severe cases, the bursae may be drained out or even removed.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is a condition marked by inflammation of the tendons. Tendonitis commonly occurs due to excessive use of the body part through repetitive motions. It typically affects the wrists, elbows, and knees. Tendonitis is also treated through the RICE method. Some patients may also be given steroid injections and advised to undergo physical therapy.
Strains
Overuse or sharp force applied to muscle or tendon can lead to a strain. Strains are common soft tissue injuries experienced by athletes. The RICE method can help treat mild strains, whereas more severe tears require surgery.
Contusions
Contusions are injuries resulting from impact from a blunt object on the skin's surface. These bruises can also be treated through the RICE method; however, more serious contusions should be shown to a doctor.
Different Approachs to Soft Tissue Injury Management
RICE stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation. This method is commonly adopted to treat milder forms of injury to soft tissues.
Rest: You must avoid putting any pressure on the affected body part until it heals completely. However, rest does not mean that you avoid movements altogether. It would help if you kept practicing physiotherapy exercises.
Ice: An ice pack can help with the pain and swelling. Keep ice packs handy if you have a soft tissue
injury.
Compression: Compression involves covering the affected area with a bandage to wrap it up. Avoid tying the bandage too tight; you may want to ask a doctor to wrap it for you.
Elevation: When lying down, elevate the affected limb on a pillow. Or, if you are sitting, rest it on a chair next to you. Never self-diagnose any injury that causes you a lot of pain. Always seek a professional medical opinion. If the RICE method does not work, your doctor may recommend surgery or medication.
While RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) was the standard for decades, current evidence supports the PEACE and LOVE protocol for better healing outcomes.[3][4][5]
In the first 2-3 days (PEACE):[3][4][5]
- Protect the area from further injury but avoid complete immobilization.
- Elevate the injured area above heart level when possible.
- Avoid anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen in the first few days, as inflammation is part of natural healing.
- Compress gently with elastic bandages.
- Educate yourself about the healing process and stay active within pain limits.
After the first few days (LOVE): [3][4][5]
- Load the area gradually with gentle, pain-free movement and exercises.
- Optimism - maintain a positive outlook as this improves recovery outcomes
- Vascularization - engage in cardiovascular exercise to improve blood flow to healing tissues.
- Exercise - progressively increase activity to restore full function
Experience the latest in medical technology from Meril
Meril is a global medical device company based in India. Founded in 2006, Meril is committed to designing and developing novel medical devices that promote efficient healing. The company manufactures a range of products, including diagnostic devices, ENT medical devices, orthopedic implants, and vascular intervention medical devices, among others.
Meril also manufactures three state-of-the-art sutures for soft tissue treatment:
Polydioxanone Suture
FILAXYN POLYDIOXANONE suture promise long-term wound support. It is designed for general soft tissue approximation and / or ligation. This suture is especially suitable for geriatric and immunocompromised patients. It has high initial tensile strength and predictable absorption.
Absorbable Suture
MITSU AB™ is a mid-term absorbable braided synthetic suture made of poly(glycolide-co-l-lactide) (90/10) coated with Triclosan, an antibacterial agent. It degrades by hydrolysis and assures predictable and reliable absorption.
Poliglecaprone Sutures
FILAPRON POLIGLECAPRONE suture offers scarless sub-cuticular suturing. There is complete mass absorption within 90 to 120 days.
Tips to prevent soft tissue injuries
Warm-up and preparation: Spend 10-15 minutes on dynamic warm-up exercises before activities. Research shows this reduces injury risk by over 35%.[6][7]
Strength and conditioning: Include exercises that strengthen muscles around joints and improve balance. Neuromuscular training programs are particularly effective.[7][8]
Gradual progression: Increase activity intensity, duration, and frequency gradually - follow the "10% rule" of not increasing total activity by more than 10% weekly.[8][9]
Proper technique: Learn correct movement patterns for your sport or exercise. Poor technique significantly increases injury risk.[8][9]
Adequate recovery: Allow 48-72 hours between intense training sessions for the same muscle groups.[9][10]
Stay hydrated and maintain nutrition: Proper hydration and nutrition support tissue health and recovery.[10]
Listen to your body: Don't ignore persistent pain or fatigue, as these often precede injuries.[9][10]
Conclusion
Soft tissue damage can be quite painful, and adequate rest is needed for you to be able to heal completely. Make sure you follow your doctor's advice, take your medicines on time, and practice the physiotherapy exercises as advised. Avoid putting pressure on the affected areas until they have healed completely. With proper rest and care, you will be able to move with comfort once again.
References
[1] http://hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/softtissue-injuries
[2] https://sma.org.au/resources/injury-fact-sheets/soft-tissue-injuries/
[3] https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/54/2/72
[4] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31377722/
[5] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3396304/
[6] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31431273/
[7] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8558815/
[8] https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0205635
[9] https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/23259671211035776?int.sj-abstract.similar-articles.9
[10] https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/769864