How Colon Cancer is Detected?
Introduction
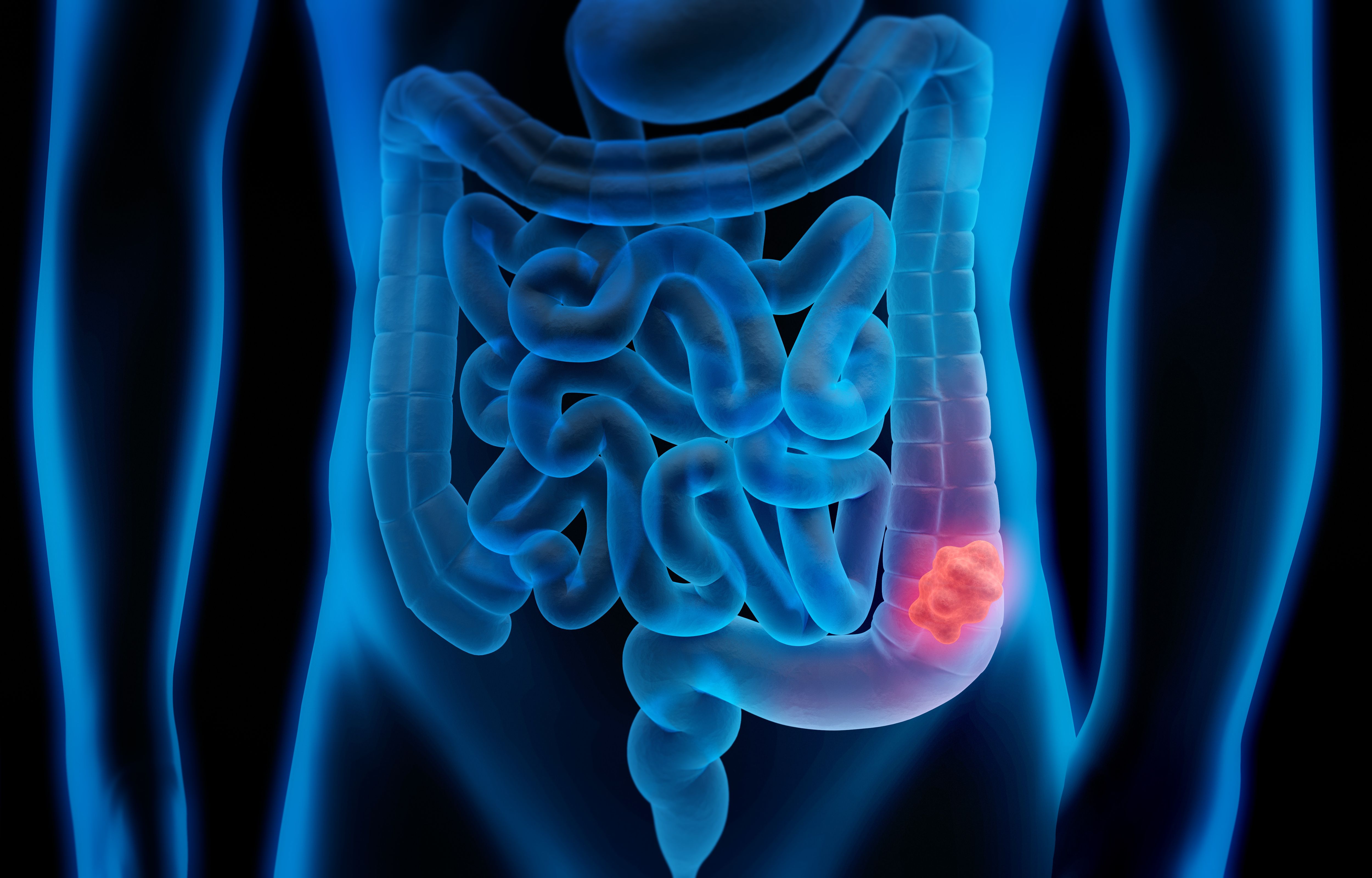
Globally, colorectal cancer is the third most prevalent cancer.
Colon cancer (colorectal cancer) is a common type of cancer, coming in at number three among cancers diagnosed around the world. While in the past, it was mostly seen in older people, recent increases are being seen in younger people as well. More than half of the cases happen in wealthier nations, which suggests that their diet and exercise habits play a role.1 Colorectal carcinoma is evolving as a key health issue even in developing countries like India. Altering lifestyle, eating habits, obesity, and lesser physical activity are additional risk factors compounding the risk in this subset of patients. Based on studies, more young adults now develop colon cancer than before, and it tends to be more aggressive in them2. For this reason, doctors must pay attention to symptoms, even when the patient is under 50. If caught at an early stage, colon cancer is treatable with good results, but a late diagnosis can result in more serious problems. For this reason, noticing warning signs early and getting treated quickly is very important.
Who Should Get Screened?
The majority of major medical groups advise that individuals at average risk begin colon cancer screening at age 45, rather than waiting until 503 as previously recommended. This shift reflects a rise in colon cancer cases among younger adults.
Why is screening important, and who should consider it?
Detecting colon cancer early provides the best chance of a cure.
Screening reduces the risk of dying from colon cancer.
- Multiple screening methods are available, each with its own advantages and limitations. Your doctor can help you choose the most appropriate one
- If a colonoscopy is selected, any polyps found during the procedure can often be removed immediately, helping prevent cancer from developing
You may be at higher risk and need to start screening earlier and more frequently if you:
Have a family history of colon cancer
Experience inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis)
Have certain genetic conditions, such as Lynch syndrome or FAP (Familial Adenomatous Polyposis)
Have had colon polyps in the past.
There are multiple screening methods, each with different pros and cons. Talk to your doctor to determine the best option for you.
If a colonoscopy is chosen, polyps can be removed during the procedure, which can prevent cancer from developing.
It may be more important for people at high risk to perform screening at an earlier age and with greater regularity.3
Diagnosing colon cancer
If you notice possible signs of colon cancer like changed bowel habits, blood in stool, weight loss or pain, your doctor will run tests to discover the problem. Since they are looking at particular issues, these tests require more steps and are not as simple as screening tests.
1) Colonoscopy4
Symptoms are the reason a diagnostic colonoscopy is done, whereas a screening colonoscopy is performed even when no symptoms are found. The doctor follows the usual procedure but carefully checks any areas that may explain what you are experiencing. Scientists take samples (biopsies) for testing in a laboratory if suspicious tissue appears.
2) Blood tests5
A colon cancer diagnosis can’t be made using blood tests alone; however, blood tests offer helpful information.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This evaluates for signs of anaemia so that tumour bleeding can be found.
- Liver Function Tests: Check the health of your liver, as colon cancer can sometimes grow in it.
- CEA (Carcinoembryonic Antigen): People with colon cancer might have higher amounts of this protein in their blood. However, sometimes the levels are high for other conditions, so it is not used to diagnose, but to watch treatment progress.
- Octo-biopsy, which finds DNA from cancerous cells in the blood, has been created but is still not widely used today.
3) Stool-based tests
- Highly sensitive fecal immunochemical test (FIT) every year
- Highly sensitive guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT) every year
- Multi-targeted stool DNA test (mt-sDNA) every 3 years
What Happens After Abnormal Results?
Follow-up Care
When certain screening tests find deviations from the normal range:
- Be calm: Sometimes, unusual results are not related to cancer
- Testing after treatment: A colonoscopy is usually used to diagnose cancer with certainty
- If a biopsy is performed, the samples are studied by a pathologist with the help of a microscope
- Staging: Following a cancer diagnosis, tests show whether it has advanced in the body
Treatment Overview
- If the cancer is in the early stages, it might be treatable with surgery alone on the affected part.
- Advanced cancer often requires using surgery, chemotherapy and/or a radiation course together.
Colon Cancer Surgery
Surgery is usually the main treatment when colon cancer is found. Colectomy is the name of the main operation which takes out the cancerous tissue in the colon.
Different Types of Colectomy Procedures.
- Partial Colectomy (Hemicolectomy): Only the part of the colon where cancer is found is removed, along with some healthy tissue around it as a precaution.
- In a Total Colonectomy, the entire colon is removed from the body (this is rare and done in certain cases).
- Remaining lymph nodes nearby are removed to see if cancer has invaded other areas
The Purpose: Get rid of the cancer but try to keep as much of your healthy colon function as possible.6
In addition to surgical resection, surgical options for colorectal cancer include:
Laparoscopic surgery
- Surgical Procedures That Are Less Invasive
- Also known as Keyhole Surgery (Laparoscopic Surgery).
- Methods: Rather than make one big cut, the surgeon performs multiple small abdominal cuts (about ½ inch each)
- Procedure: Surgical tools and a tiny camera enter the body via the small cuts near the belly button
Benefits:
- Smaller scars
- Surgery usually leads to less discomfort.
- Most commonly, a hospital stay is only two to three days rather than five to seven days.
- Quick return to their regular routines
- Fewer opportunities for getting infected
Robotic Surgery
Similar in some ways to laparoscopic surgery, in that robotic arms are used for greater precision.
Few people are eligible for minimally invasive surgery. The factors used in prognosis are tumor size, where it is located and if cancer has reached other body areas.7 MIRUS™ Circular Stapler gives phenomenal clinical performance, usability experience and adaptability with wide range of Lumen Sizes for anastomosis. This Circular Stapler is a sterile single patient use, mechanical instrument design reflects three decades of experience drawn from leading Bariatric, Colorectal and General Surgeons across the globe.
Colostomy for rectal cancer
A small opening called a stoma is made in your belly by the surgeon
A segment of the colon gets brought to the copy site.
After surgery, you will have a pouch hanging on your skin for waste collection.
Kinds of Colostomy:
Temporary: Not meant to be permanent; it may be reversed after a few months as your colon heals after surgery
Permanent: When the surgeon has to remove the lower colon or rectum completely
It is good to keep in mind:
Most colon cancer patients are able to avoid interventions like a colostomy.
With current surgical practices, the need for permanent colostomies has gone down a lot.
For most people, getting back to their routines comes quite smoothly when needed.
Trained nurses (ostomy nurses) teach and assist patients after their operation.8
Treatment for Advanced Disease
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or cryoablation.
If colon cancer ‘metastasizes,’ meaning it spreads to other parts of the body, a number of treatment options may be used.
Surgical Removal:
Liver Resection: The surgeon removes only the liver area that contains cancer.
To treat lung cancer, the surgeon may remove cancerous regions from the lungs.
In many cases, radiotherapy gets better results when it is used together with chemotherapy.
Procedures that Don’t Require Surgery:
In Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA), heat is used to destroy tumor cells
The procedure called cryoablation freezes and kills cancer cells.
Microwave Ablation: Heats a person’s body with microwaves to shrink cancer cells
In times these concepts are applied:9
Tumors are often found to be either too small or in too many locations for surgery.
Given the patient’s condition, there is too much risk involved in having surgery.
Endoscopic surgery is gentler than cutting the skin and healing takes less time.
May not get rid of all cancer cells; may not work for tumors in every part of the body
Conclusion
Early detection gives good opportunities for colon cancer treatment and control. Screening for polyps every two years starting at 45 has a good chance of removing them early. People have a range of ways to be screened, from easy at-home tests to detailed colonoscopies.
Detecting cancer early often means that the cancer can be treated before symptoms show up. Current therapies are both stronger and gentler to the body than in earlier years. Discuss screening with your doctor, follow their advice about getting tests and contact your doctor as soon as you observe any worrying symptoms of colon cancer. Given that it is catchable early, the greatest defense against colon cancer is regular testing.
References
1. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11290395/
2. https://www.nccn.org/patients/guidelines/content/PDF/colorectal-screening-patient.pdf
3. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/colorectal-cancer-screening
4. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3377498/
5. https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2024/10/colon-cancer-screening.html