Active Robotics in Knee Replacement Surgeries for varying patient anatomies
Introduction
How different is traditional knee replacement surgery from robot-assisted knee replacement? A typical question for every patient or caregiver before planning knee replacement. Quite understandable is their concern when it comes to taking a major life decision of replacing one's knee joint with an artificial implant for good. If viewed from a broader perspective, both surgeries aim to relieve knee pain, immobility, and discomfort of the diseased knee joint. However, the difference lies in their approach to accessing knee joints, the use of surgical devices, the degree of accuracy and operational effectiveness, the role of human intervention and chances of human error, and the involvement of artificial intelligence in the operating room.
Robotics are a game-changer, offering multiple advantages of precision, accuracy, efficiency, and control in the surgical performance of healthcare professionals. These robots are increasingly commanding attention and acceptance in surgical interventions treating various diseases and medical conditions requiring access to the inside of the human body.
This blog discusses how robotic platforms in knee surgeries cater to the clinical needs of the varying patient anatomies to help understand the reasons for its wide acceptance and expansion in healthcare.
Robotics Platform for Knee Surgeries
From the initial goal of minimizing human error and maximizing surgical accuracy and precision, robotics has come a long way since then. With each generation of technological upgradation, it has evolved with promising benefits aimed at changing the landscape of orthopedic surgeries. Knee replacement has been performed routinely in all orthopedic surgeries, and the need for surgical precision, accuracy, and efficiency remained at the core of introducing robotics in orthopedics.
The role of traditional knee replacement can never be undermined. The need for robot-assisted surgery arose due to physical, mental, and technical variables inherent in exclusively surgeon-operated knee replacement. These variables often affect surgical performance, leading to inaccurate implant fixation and positioning, poor limb alignment, ligament tensioning, damage to scar tissue, and imbalance in flexion-extension gaps. This further results in poor bone resection, implant functionality, and surgical and patient outcomes.
Robotics aims for precision in bone resection, which is fundamental to overcoming all the limitations of traditional knee replacement surgery. Depending on the method for bone resection, robot-assisted surgery could be fully active or semi-active.
Benefits of Active Robotics in Knee Replacement
Fully active robotics implies that all pre-programmed operations of bone resections, be they femoral or tibial, are performed exclusively by the robots. In the case of semi-active robotics, the surgeon is guided by the robotic arm in bone resection within the assigned range based on the preoperative plan. The surgeon is in the driver's seat, conducting the most complex operations with precision and accuracy with the help of the robot's assistance.
Robotic platforms for knee replacement provide a patient-centric and personalized surgical experience. Each knee surgery is performed with specific anatomical information of the patient fed into virtual 3D models using computer software. Various diagnostic software, like CT Scan, MRI, radiographs, or intraoperative imageless mapping generate these 3D images that enable the surgeon to plan the bone resection for each patient before going to the surgical table.
Every patient's anatomy is different, and so are the surgical requirements. Active robotics caters to the specific and personalized clinical needs of the patient through-
- Creating a virtual 3D model of the patient's knee that enables the surgeon to plan bone resection, implant sizing, limb alignment, range of motion, and potential gaps inside and outside the knee post-surgery.
- Providing an accurately and perfectly crafted balanced knee through preoperative planning using 3D images, thus enhancing stability and mobility of the treated knee.
- Haptic technology that creates a physical experience of touch for virtual displays on software devices. In robot-assisted knee replacement, the virtual images are synced with a robotic arm, enabling the surgeon to precisely remove the designated area of the diseased bone without damaging the tissue, ligaments, or bones. Any deviation from the planned resection is restricted by the robot when the device automatically stops.
- Perfect implant positioning, ensuring accurate implant size, positioning, and range of motion by micro-adjustments that meet the patient's anatomical needs.
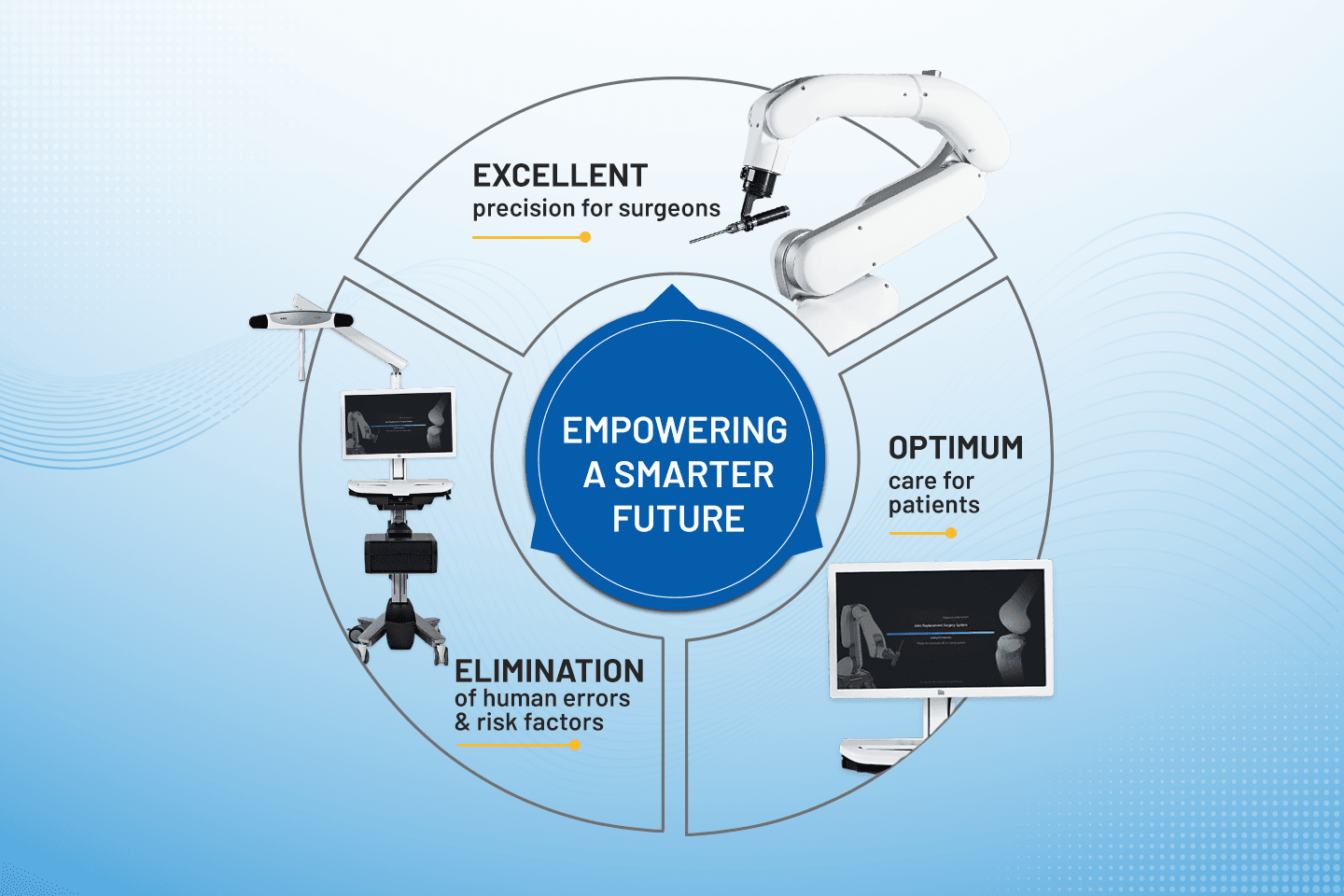
CUVIS from Meril
CUVIS JOINT ROBOTIC SYSTEM from Meril is India's First Robotic Surgery System. It is the most advanced surgical cutting-edge robotic technology supporting surgeons with personalized preplanning and precise cutting for predictable and consistent results. Active robotics is a user-friendly, flexible, accurate, and safe system that uplifts lives. It is a step towards a smarter future of consistent and predictable surgical outcomes and enhanced patient care.
Conclusion
While addressing the limitations of traditional knee replacement surgery, the robotic platform provides added efficacy, new efficiencies, precision, and accuracy to the surgical procedure, ensuring less painful, prompt, and faster recovery, paving the way for improving the lives of millions. Being stress-resistant, invulnerable to emotional responses, and dexterous with high maneuvering skills while performing complex operation moves, robots reduce potential human errors and enhance surgical efficacy and performance. They offer patient-centric and personalized knee replacement treatment that caters to the anatomical needs of every patient.