Understanding Peripheral Arterial Disease Treatment with Below the Knee (BTK) Scaffolds
Introduction
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a serious condition that can cause pain, wounds, and even limb loss due to poor blood flow in the legs and feet. For many living with PAD, especially when arteries below the knee are affected, daily life can be challenging. Recent advances in vascular medicine, such as Below the Knee (BTK) scaffolds, provide new hope. These innovative devices help restore blood flow, reduce symptoms, and improve quality of life for patients with below-the-knee PAD. This article explores how BTK scaffolds are changing the outlook for PAD patients.1
What is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)?
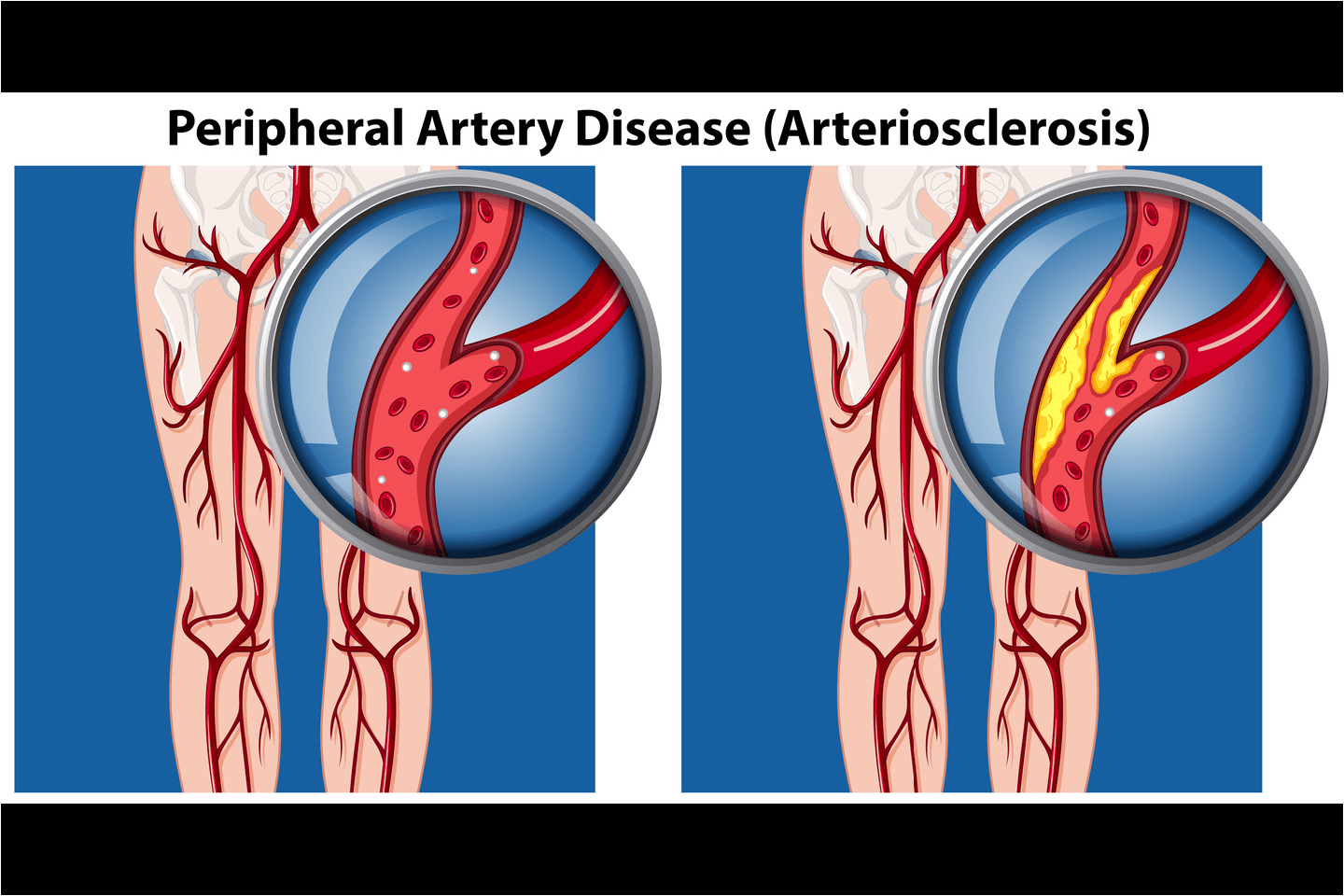
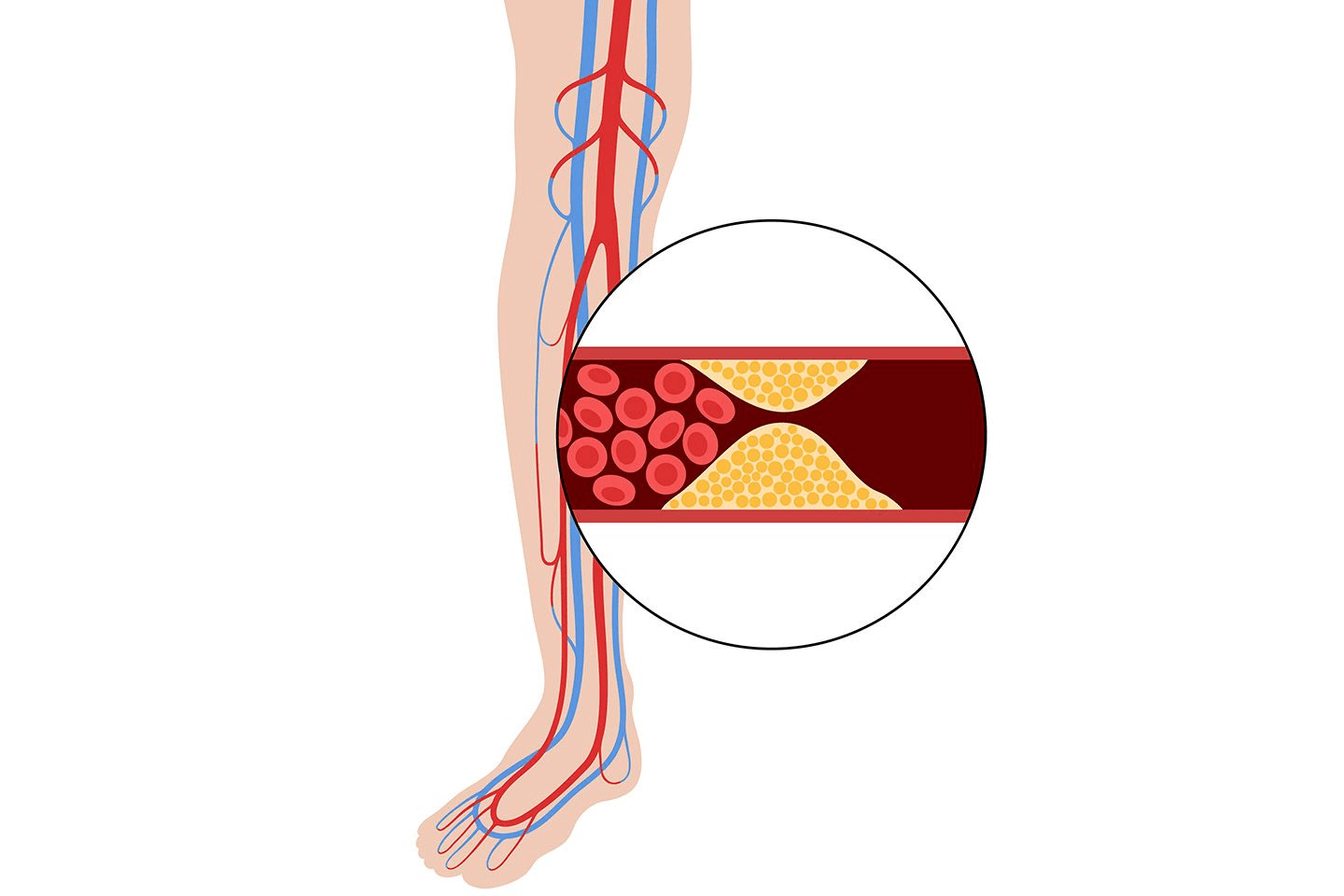
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) happens when fatty deposits, called plaque, build up inside arteries, narrowing or blocking blood flow to the legs and feet. This can cause pain while walking, slow-healing wounds, and, in severe cases, tissue damage or amputation. If left untreated, PAD can lead to severe pain, ulcers, gangrene, and even amputations. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications and preserving mobility.2
While significant advancements have been made in treating PAD, developing below-the-knee (BTK) scaffolds is revolutionising how we manage this condition. BTK scaffolds offer new hope for patients by providing targeted and innovative solutions to improve treatment outcomes.
What are BTK Scaffolds?
Below the Knee (BTK) scaffolds, also known as stents or endoprosthesis, are small, tube-like devices that help open and support arteries below the knee that have become narrowed or blocked. Inserted through a minimally invasive procedure, these scaffolds restore blood flow to the lower leg and foot, helping patients heal wounds, reduce pain, and lower the risk of limb loss.3 Unlike stents used in coronary arteries, BTK scaffolds are designed to address the unique challenges posed by the smaller and more intricate arteries found in the lower leg.
Types of BTK Scaffolds and Their Characteristics
Several BTK scaffolds are available, each with distinct characteristics catering to specific patient needs. There are three main types of BTK scaffolds used in below-the-knee PAD treatment:
● Bare-Metal Stents (BMS): Simple metal tubes that open the artery.
● Drug-Eluting Stents (DES): Release medication to help prevent the artery from narrowing again.
● Bioresorbable Scaffolds (BRS): Temporary scaffolds that dissolve over time, reducing long-term risks and allowing natural healing.
Your doctor will recommend the best type based on your needs and health history.4
All types of BTK scaffolds have their advantages, and the choice depends on the patient's condition and medical history.
How BTK Scaffolds Work & Benefit PAD Patients
BTK scaffolds are placed using a minimally invasive procedure called endovascular intervention. A thin tube (catheter) is guided to the blocked artery, and once deployed, the scaffold expands, pushing the plaque against the artery walls, and remains in place, acting as a support structure to maintain blood flow. Some scaffolds release medication to keep the artery open longer. For patients, this means less pain, quicker recovery, and a lower risk of amputation than traditional surgery.5
The benefits of BTK scaffolds in PAD treatment are numerous:
- They provide a less invasive alternative to traditional open surgeries, significantly reducing patient discomfort and recovery time.
- They provide targeted treatment, precisely addressing the affected area and minimising damage to healthy tissues.
- BTK scaffolds have shown promising long-term results in preventing the recurrence of arterial blockages, preserving limb functionality, and finally improving patients' overall quality of life.
Advancements in BTK Scaffold Technology
- Better Materials and Smarter Designs: Advancements in material science have led to the development of novel BTK scaffold materials for BTK scaffolds that are safer and less likely to cause problems in the body. The design improvements make these tiny scaffolds more flexible, so doctors can easily guide them through tortuous arteries, and enhanced radial strength to ensure the scaffold remains securely in place.
- Bioresorbable and Drug-Eluting BTK Scaffolds: Bioresorbable BTK scaffolds are made to slowly gradually dissolve inside the body over time, so no permanent metal is left behind. This reduces the chance of long-term problems and makes future treatments easier if needed. Drug-eluting BTK scaffolds slowly release medicine that helps keep the artery open longer by preventing it from narrowing again. These scaffolds have revolutionized treatment outcomes by reducing restenosis rates significantly and improving the long-term patency of the treated arteries.
- How Nanotechnology Helps: Nanotechnology has made notable contributions to enhancing the performance of BTK scaffolds. Incorporating nanoparticles into the scaffold's coating makes drug delivery more precise and targeted. Moreover, nanomaterials offer improved mechanical properties and better biocompatibility, further optimising the scaffold's overall effectiveness.
Efficacy
● Comparative Analysis with Traditional Treatment Methods: Compared to traditional treatments like bypass surgery or balloon angioplasty, BTK scaffolds are less invasive, have fewer complications, and allow faster recovery. They are beneficial for patients who cannot undergo open surgery. Studies show that BTK scaffolds improve blood flow, reduce pain, and help heal wounds in patients with peripheral artery disease below the knee.6
● Long-Term Benefits for Patients: Long-term studies show that patients treated with BTK scaffolds experience better blood flow, less pain, and fewer ulcers and infections. Most importantly, BTK scaffolds help many patients avoid amputation, enhancing their overall quality of life.7
Conclusion
BTK scaffolds represent a significant advance in Peripheral Arterial Disease Treatment, especially for those with blockages below the knee. These medical devices offer targeted, effective, and less invasive solutions that improve blood flow, reduce pain, and help patients keep their limbs. As research continues, BTK scaffolds will likely play an even greater role in improving the lives of people with PAD.8
FAQs
Q: How do BTK scaffolds work, and what benefits do they offer in PAD treatment?
A: BTK scaffolds are placed inside narrowed arteries below the knee through a minimally invasive procedure called endovascular intervention. A thin catheter tube is inserted through a small incision and guided to the blockage site. The scaffold then expands, pushing plaque against the artery walls and holding the artery open to restore blood flow. Benefits include less invasive treatment, precise targeting of the affected artery, faster recovery, and promising long-term results in preventing artery re-narrowing and improving limb function.
Q: What advancements have been made in BTK scaffold technology to enhance performance?
A: Recent advances include new materials that improve how well scaffolds interact with the body, making them safer and more flexible. Bioresorbable scaffolds, which dissolve over time, reduce long-term complications. Drug-eluting scaffolds slowly release medication to prevent the artery from narrowing again. Additionally, nanotechnology has improved drug delivery and scaffold strength, making treatments more effective.
Q: How do BTK scaffolds compare with traditional treatment methods, such as bypass surgeries or balloon angioplasty?
A: Compared to traditional methods, BTK scaffolds generally have fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times. Their minimally invasive nature makes them suitable for patients who may not be candidates for open surgery. Studies show that BTK scaffolds improve blood flow, reduce pain, and help heal wounds, significantly enhancing patients’ quality of life.
Q: Are BTK scaffold treatments suitable for all PAD patients, and what should patients consider before opting for this procedure?
A: BTK scaffold treatment is not suitable for all PAD patients. The best treatment depends on factors like the severity and location of artery blockages, overall health, and medical history. It’s important to consult with a qualified vascular specialist who can assess your condition and discuss the potential benefits and risks. Together, you can decide if BTK scaffolds are the right choice for your Peripheral Arterial Disease treatment.
References
1https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circresaha.116.303849
2https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17223489/
3https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33547627/
4https://www.jscai.org/article/S2772-9303(22)00007-2/pdf
5https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4504240/
6https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18502084/
https://evtoday.com/articles/2011-aug/below-the-knee-drug-eluting-stents